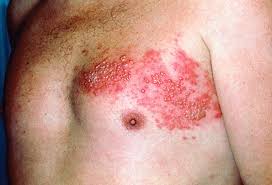
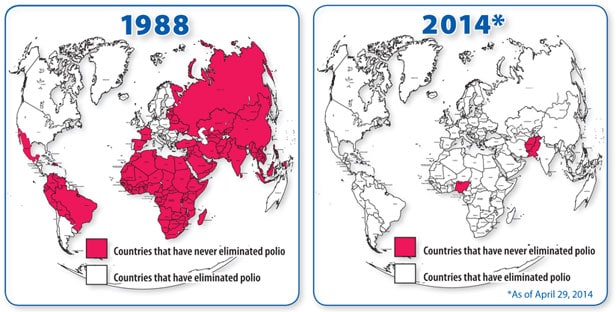
Ever since a poorly executed research article was published saying that vaccinations cause autism, people have started to become anti-vaxers. Even though this conclusion has since been proven to not be true, people still continue to not get vaccinated. Companies, like Facebook, have started taking a stand against these anti-vaccination posts.
What is Facebook doing?
To help this anti-vaccination movement, Facebook declared in March that they would try to limit the spread of misinformation about vaccines. Facebook has since removed anti-vaccination groups from peoples recommendations, and has removed anti-vaccination ads. Although Facebook cannot delete people’s anti-vaccination posts, they are making these types of posts harder to search on Facebook.
Facebook and other companies started limiting anti-vaccination content because they were getting a lot of pressure from legislators, and organizations. The American Medical Association wrote a letter addressing all social media companies telling them that they should start monitoring anti-vaccination posts. The American Medical Association wrote: “With public health on the line and with social media serving as a leading source of information for the American people, we urge you to do your part to ensure that users have access to scientifically valid information on vaccinations, so they can make informed decisions about their families’ health”.
I think what Facebook is doing is helping overall. In today’s society, people will believe anything they see on the internet, so if Facebook can block any misinformation about vaccinations it will be a big help. Billions of people are on Facebook, and I believe that what Facebook is doing it great, but if they could go one step further and advertise valid healthcare websites with truthful information about vaccines, I think the anti-vaccination movement would start to dwindle down.
The governments role
As the anti-vaccination movement continues, the government is trying to take over more of a role in stopping anti-vaxers. But, some groups are saying that the government shouldn’t have a role at all.
In 2015, California became the first state to get rid of exemption clauses from school vaccination laws. This has led to the growing of California’s vaccination rate. But, those families that still don’t want to vaccinate their children have started moving to private and charter schools to avoid the vaccination laws.
Another example of a government role in this movement occurred in New York. In April, New York had a bad measles outbreak and the mayor responded by ordering mandatory vaccinations for the community that started the outbreak. The Washington Post considered this the strongest state response to a public health crisis in decades.
There have also been multiple wins and loses (of law suits) for the anti-vaccination community this year. In march, multiple parents lost in a lawsuit to try and get their unvaccinated children readmitted to school. Then, in the same community in April a judge got rid of a ban that was not letting unvaccinated children into public places.
I believe that in the future, and as this issue gets worse, the government will clearly state their role, and make new laws regarding their decision. In my opinion, I believe the government should make laws regarding the mandatory vaccination of children because vaccinations don’t just help the child, they also help those around the child that might not be able to get vaccinated for health reasons. The government cannot refute the fact that unvaccinated children are a threat to public health, so I think that if the government steps in, it could be a huge step to ending the anti-vaccination movement.